From the article:
Scientists have caught a once-in-a-billion-years evolutionary event in progress, as two lifeforms have merged into one organism that boasts abilities its peers would envy. Last time this happened (1.6 billion years ago), certain advanced cells absorbed a type of bacteria that could harvest energy from sunlight. These became organelles called chloroplasts, which gave sunlight-harvesting abilities, as well as a fetching green color, to a group of lifeforms you might have heard of – plants.
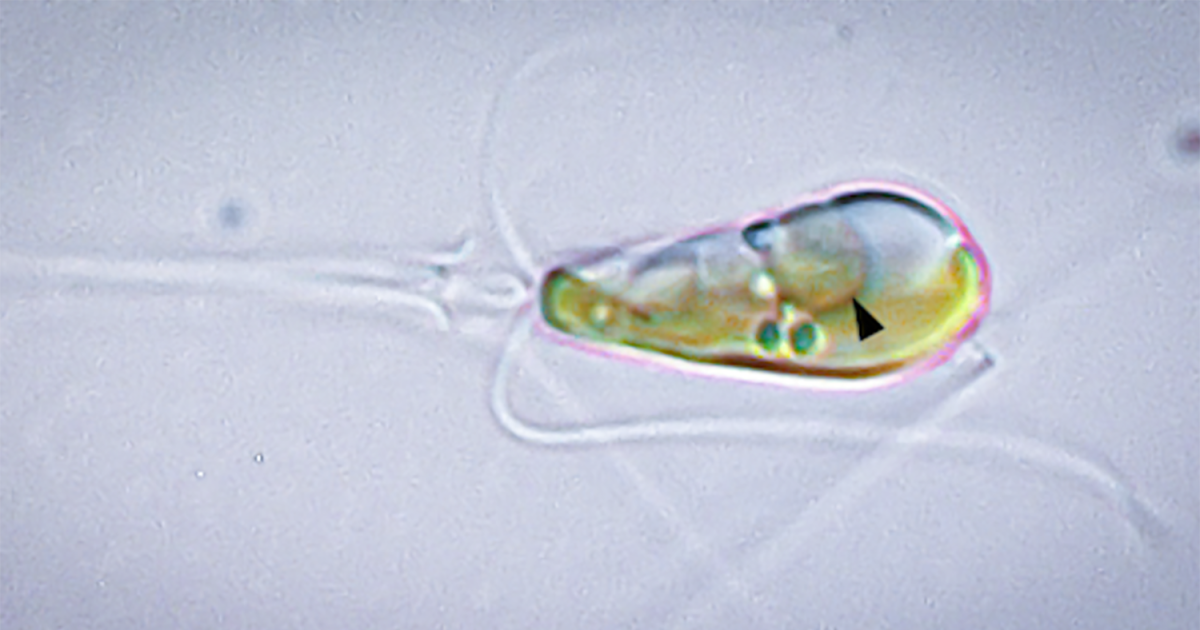
And now, scientists have discovered that it’s happening again. A species of algae called Braarudosphaera bigelowii was found to have engulfed a cyanobacterium that lets them do something that algae, and plants in general, can’t normally do – “fixing” nitrogen straight from the air, and combining it with other elements to create more useful compounds.


No, the symbiotic relationship means that the bacteria live in/on the plant, much like we have a gut biome of organisms that are discrete from us, but have symbiosis with us.
The article is about a bacterium becoming engulfed within an algal cell and slowly becoming an organelle of that cell.
This process begins as a type of symbiosis, but at the end of it you would no longer call it symbiotic, as it ends as a single organism.
The breathless yammering about “the last time this happened we got plants” seems a little much though. The last time this happened that we know of was 1.5 billion years ago and we got plants. The fact we’ve caught it in the act right now sounds like this might just be a much more common phenomenon than we thought.
The article says
It’s possible the only reason we’re aware of these events is because they were massive breakthroughs. After watching it happen, we may have more information about how to spot other times it has happened.